PCOS is known as “polycystic ovarian syndrome” or also known as “Stein- leventhal syndrome”.
PCOS is common in women of reproductive age group. It’s prevalence is as high as 25%. It is a disease of long term. PCOS is most common endocrine disorder among women of reproductive age group. In India, 1 among every 5 women suffer from PCOS. About 25% of normal women have polycystic ovaries but are asymptomatic, therefore there is a criteria to diagnose a women suffering from PCOS.
Most important risk factor of PCOS is obesity, therefore patients of PCOS are advised to keep a control over their weight and maintain it to a normal limit (PCOS can also occur in non obese woman).
Clinical representation of PCOS:
• Obesity
• Infrequent menses since menarche
• Mild hair growth over chin and upper lip
• Acne
• Acanthosis nigricans – Dark valvety pigmentation over nape of neck, underarm or below breast (acanthosis nigricans is a feature of insulin resistance).
Pathophysiology:
• It occurs due to peripheral insulin resistance.
• This causes hyperinsulinemia which causes stimulation of stroma and theca cells resulting in increase in androgen production by the ovaries.
• This decreases Sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG).
• Number of free androgens in circulation increases.
• This contributes to more peripheral insulin resistance.
Androgen produced in ovaries is known as androstenedione (testosterone increases).
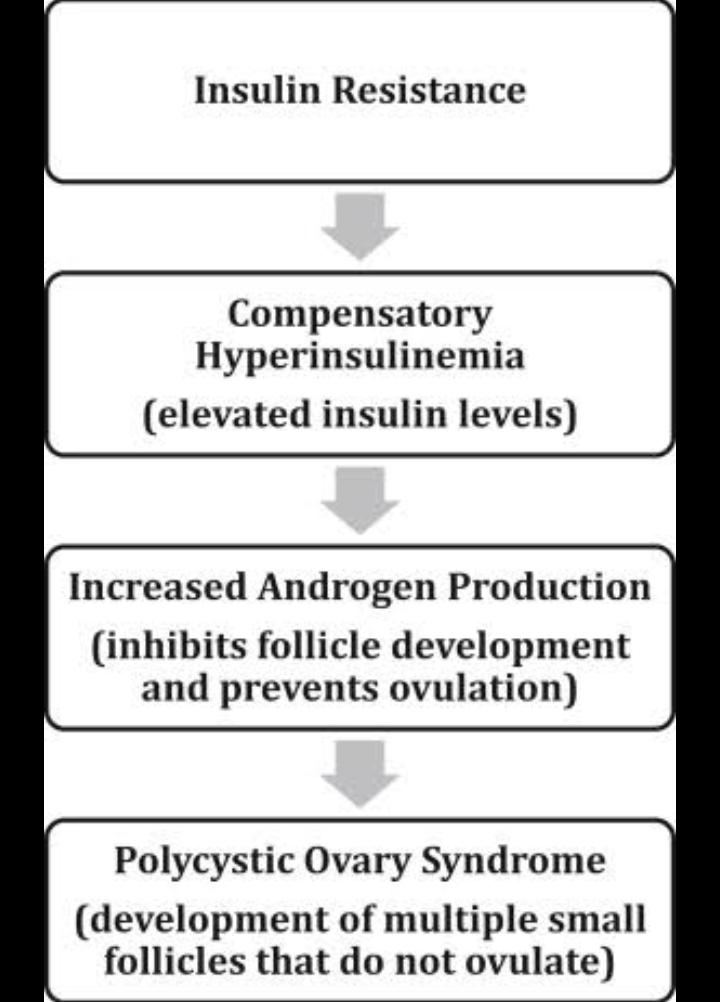
Increased androgen production causes:
• Disturbed follicular growth which causes increased ovarian stroma.
• Chronically elevated estrone levels which causes chronically elevated LH levels
• This causes anovulation.
• Follicles recruited in every cycle never becomes dominant follicle and they die .
• They add to the ovarian stroma and increases stromal volume.
• Ovary becomes bulky and causes polycystic appearance of the ovaries.
Anovulation causes:
• Menstrual cycle abnormality
• Infertility
• Oligomenorrhea followed by increased (heavy) bleeding or complete amenorrhea.
• Hyperplastic endometrium
This excessive endometrium formed when outgrows, it’s blood supply causes shedding off of endometrium causing excessive bleeding (for about 10 – 15 days).
Differential Diagnosis:
• PCOS
• Obesity
• Hypothyroidism
• Hyperprolactinemia
• Non – classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia (not seen often – usually present in girls before or around puberty)
Therefore, before making diagnosis of PCOS we should rule out hypothyroidism and hyperprolactinemia.
Rotterdam criteria for diagnosis of PCOS:
3 criteria are mentioned in it, out of which 2 criterias need to be fulfilled for diagnosis of PCOS. These criteria are mentioned below:
1. Menstrual cycle abnormalities – amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea
2. Hyperandrogenism
• Clinical – hirsutism, acne hair loss
• Biochemical – increased serum testosterone levels
3. USG appearance of Polycystic ovaries
• Presence of 12 or more follicles in either ovary measuring 2-9 mm.
• and / or increased ovarian volume.
Hormonal changes :
• Serum testosterone level increases
• LH level increases
• Serum androstenedione level increases
• SHBG level decreases
• Total estrogen increases
• LH : FSH ratio > 2 : 1
• Reversal of estrogen : estradiol ratio
Clinical Management :
• Lifestyle modification (as in diabetes mellitus)
• Weight reduction
• Say no to refined carbohydrate
• Say no to smoking
Drug Treatment :
To counter the problem of insulin resistance Metformin drug is given.
Now women is treated according to the state of women which is classified as follows:
1. If Woman do not want to conceive at that moment –
Drug of choice is OCPs (combined oral contraceptive pills).
OCPs causes feedback inhibition of the pituitary which decreases FSH and LH production by the pituitary which in turn suppresses the ovarian follicular growth.
Only the endometrial cycle goes on in response to estrogen and progesterone in the OCPs.
Now when the woman stops taking hormonal pills for 1 week, shedding off of endometrium occurs.
Therefore, OCPs regularises periods, prevents endometrial hyperplasia and also helps in hirsutism.
2. If Woman wants to conceive –
Drugs to induce ovulation are given
In this case drug of choice is – Letrazole (aromatase inhibitor)
None of the drug listed above should be taken without proper consultation of the doctor.This post is just for educational purpose and not for any clinical practice.
Contributor- Medico Eshika Keshari





Nice
👏