Cellular adaptation is the morphological changes adapted by cells due to increase demand and then revert back to normal after removal of stress. The most important example of cellular adaptation is hypertrophy and hyperplasia of uterus during pregnancy which becomes normal after delivery.
Some important physiological changes in pregnancy are listed below-
• Uterus undergoes both myometrial hypertrophy and hyperplasia under the effect of estrogen during pregnancy (hypertrophy>>hyperplasia).
• Breast undergoes only hypertrophy of ducts (due to estrogen) and hypertrophy of glands (due to estrogen and progesterone both).
Some increased metabolic demands in pregnant ladies are listed below-
• Thyroid hormone production increases.
• BMR increases.
• Oxygen consumption increases.
• Oxygen carrying capacity increases.
Hemodynamic adjustments and changes during pregnancy:
• Increased blood volume (by about 30-40%)
It is due to water retention (due to estrogen stimulation on renin angiotensin system of kidney and lowered osmotic threshold for thirst).
• PVR decreases (peripheral vascular resistance).
• Vasodilation (due to estrogen, progesterone, relaxin and NO).
• Palmar erythema
• Spider angioma
• Sensation of heat, sweating and nasal stuffiness.
• Physiological edema which is relieved with rest.
• Clotting factor increases (except CF11 and CF13) leading to hypercoaguable state.
• In order to counter this hypercoaguable state a protective mechanism occurs which is known as hemodilution.
-RBC mass increases by about 20-30%
-Plasma volume increases by 40-50%
-Blood volume increases by 30-40%
Above 3 factors causes hemodilution which is a protective mechanism which is explained in the following diagram below:
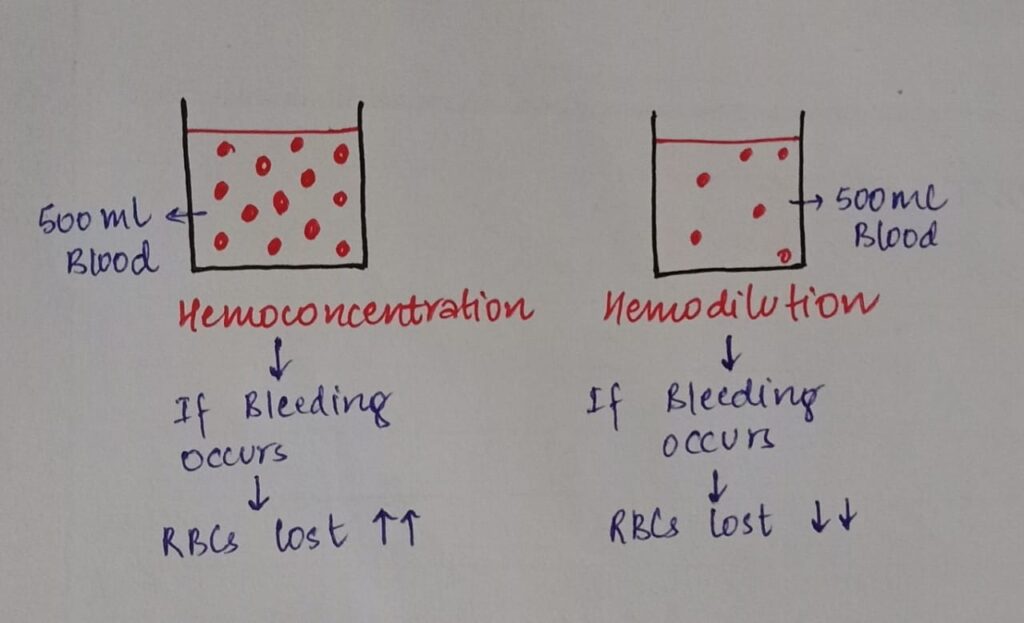
Changes due to hemodilution:
• Hb concentration decreases.
• Hematocrit (PCV) decreases
• Platelet count decreases
• Plasma protein concentration decreases
(Total protein amount increases)
Iron metabolism during pregnancy:
• Iron requirements increases
• Total Fe required is about 1000mg
• Total Fe required by foetus is about 300mg
• Physiological anemia in pregnancy due to hemodilution (starts at about 7-8 weeks and reaches maximum by about 32 weeks)
Therefore Hb is checked in pregnant ladies in each trimester.
Fe that needs to be absorbed in blood :
• 1st half of pregnancy = 3-4mg/day
• 2nd half of pregnancy = 6-7mg/day
Supplements of oral folic acid (OFA) is started form 2nd trimester (due to increased demands and also due to nausea and vomiting in 1st trimester).
Cardiovascular changes:
• Cardiac output increases
-Starts by about 5 weeks
-Maximum at 28-32 weeks
-During labor CO increases by additional 50%with each contractions.
-Immediately post partum after delivery CO increases by extra 80%
• Heart rate increases
• Stroke volume increases
• BP decreases (PVR increases)
Supine hypotension syndrome:
When pregnant woman lies down in supine position, gravid uterus is dextrorotated causing IVC compression which leads to decreased venous returns, hence causing decrease in cardiac output.
Physical changes on CVS examination:
• apex beat at 4th intercoastal space lateral to mid clavicular line.
• Loud heart sound.
• S3 may be heard.
• Exaggerated splitting of S1.
• Ejection systolic murmur hoti grade 2.
• Straightening of left border of heart.
Remaining part of maternal adaptation to pregnancy will be explained in the upcoming post
Contributor- Medico Eshika Keshari





Nice 👌👌
Nice content