Introduction
The pelvis is the lower part of the torso. It’s located between the abdomen and the legs. This area provides support for the intestines and also contains the bladder and reproductive organs
The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor.The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones.
The pelvic bone or innominate bone
The hip bone comprises the three parts; the ilium, pubis and ischium. Prior to puberty, the triradiate cartilage separates these parts – and fusion only begins at the age of 15-17.
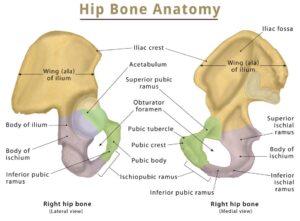
Together, the ilium, pubis and ischium form a cup-shaped socket known as the acetabulum (literal meaning in Latin is ‘vinegar cup‘). The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum to form the hip joint.
The left and right hip bones (innominate bones, pelvic bones) are two irregularly shaped bones that form part of the pelvic girdle – the bony structure that attaches the axial skeleton to the lower limbs.
The hip bones have three main articulations:
Sacroiliac joint – articulation with the sacrum.
Pubic symphysis – articulation between the left
and right hip bones.
Hip joint – articulation with the head of femur.
ANATOMICAL LAND MARKS OF HIP BONE
THE ILLIUM
liac Crest
The iliac crest is a broad convex ridge forming the upper end of the ilium. It can be felt in the living at the lower limit of the flank
It has two ends the anterior one is known as ANTERIOR SUPERIOR ILIAC SPINE (ASIS) and the posterior end is known as POSTERIOR SUPERIOR ILIAC SPINE
Gluteal surface
Gluteal surface is the outer surface of the ilium, which is concave is convex in front and concave behind, it is divided into four areas by three gluteal line
Iliac fossa
Iliac fossa is the largest concave area on the inner surface of the ilium ,situated in front of its medisl border. It lateral wall of the false pelvis
Sacropelvic surface
Sacropelvic surface is the uneven area on the inner surface of the ilium, situated behind its medial border. It is subdivided into three parts; the iliac tuberosity, the auricular surface and the pelvic surface. The iliac tuberosity is the upper, large, roughened area, lying just below the dorsal segment of the iliac crest. It is raised in the middle and depressed both above and
below. The auricular surface is articular but
pitted. It lies anterior inferior to the iliac tuberosity. It articulates with the sacrum to form the sacroiliac joint. The pelvic surface is smooth and lies anterior inferior to the auricular surface. It forms a part of the lateral wall of the true pelvis. Along the upper border of the greater sciatic notch, this surface is marked by the preauricular sulcus. This sulcus is deeper in females than in males.
THE PUBIS
Superior ramus
It extends from the the body of the pubis to the acetabulum , above the obturator foramen .it has three borders and three surfaces
The superior border is known as PECTENIAL LINE
And the anterior border is known as OBTURATOR CREST
the inferior border is sharp and forms the upper margin of the obturator foramen
Inferior ramus
It extends from the body of the pubis to the ramus of the ischium, medial to the obturator foramen.it unites with the ramus of the ischium to form the conjoined ischiopubis rami
THE ISCHIUM
this is a thick massive mass of the bone that lies below and behind the acetabulum .it has
Two ends – upper and lower
Three borders – anterior ,posterior and lateral
Three surfaces – femoral ,dorsal and pelvic
THE ACETABULUM
It is a deep cup-shaped hemispherical cavity on the lateral aspect of the hip bone, about its centre It is directed laterally, downwards and forwards,The margin of the acetabulum is deficient inferiorly,this deficiency is called the acetabular notch .It is bridged by the transverse ligament. The nonarticular roughened floor is called the acetabular fossa. It contains a mass of fat which is lined by synovial membrane. A horseshoe-shaped articular surface or lunate surface is seen on the anterior, superior, and posterior
parts of the acetabulum. It is lined with hyaline
Cartilage
THE OBTURATOR FORAMEN
This is a large gap in the hip bone, situated
anteroinferior to acetabulum, between the pubis and the ischium.It is large and oval in males, and small and triangular in females
It is closed by the obturator membrane which is
attached to its margins, except at the obturator
groove where the obturator vessels and nerve pass out of the pelvis
Anatomical difference between the male and female pelvis
The general structure of the female pelvis is thinner and less dense, in comparison to the thick and heavy male pelvis, which is designed to support a heavier body build.
The true pelvis is wide and shallow in the female, and the pelvic inlet, also known as the superior pelvic aperture, is wide, oval and rounded.
While in the male it is heart shaped, and narrow. A male pelvis has a v-shaped pubic arch that is approximately <70°.
The pubic arch is usually wider in the female pelvis at about >80°.
The coccyx in the male pelvis is projected inwards and immovable while a female pelvis has a flexible and straighter coccyx.
A lateral view of the female pelvis also reveals the relationships between the urogenital and reproductive organs.
Contributor- Medico Shashank Gupta




