Vitamins are organic proteinaceous compounds required in small amounts for maintenance of health and normal growth that are not synthesized in the body and must be obtained from diet
Vitamins are categorised in mainly two group
Fat soluble : A,D,E,K
Fat insoluble : B,C
VITAMIN A
It is derived from carotenoids which are converted in body to form retinol
The active components of retinol becomes Retinal and retinoic acid
•Retinol has its role in aiding vision
•Also aids production of glycoproteins thus maintaining mucous membrane and skin .Or we can say it is found to be helpful in maintaining the integrity of epithelial tissue
Deficiency symptoms –
Hyperkeratosis of follicles resembling goosebumps
Night blindness
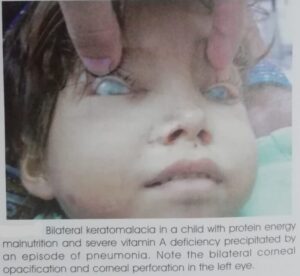
Hyperkeratinization of cornea can also lead to opacity of cornea in severe cases
Loosening of integrity of respiratory and intestinal mucosa which can result into malnutrition
Treatment and prevention
Dose of 100000 IU is given with measles vaccine at 9 months
200000 IU with DPT booster vaccine at 15-18months
In children less than 6 months ,6 -12 months and >1 years respectively:Specifics treatment includes oral vitamin A at doses of 50000 IU ,100000 IU and 200000 IU
VITAMIN D
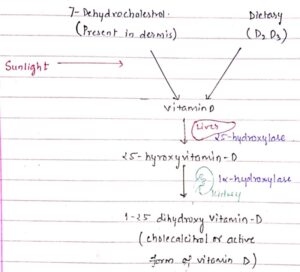
Naturally formed by skin on exposure to UV -B rays ,then from skin it goes into liver
From diet it gets absorbed by duodenum and gets stored in liver
Two forms of vitamin D are present
D2 – ergocalciferol – plant origin
D3 – cholecalciferol – animal origin
Being a fat soluble vitamin its absorption decrease with the condition in which fat absorption is affected,absorption of fat requires bile and pancreatic juice ,so any pathology involving insufficient bile production or pancreatic juice are going to affect vitamin D levels
In Fact all fat soluble vitamin deficiency can occur in malabsorption syndromes
Kidneys play an important role in activating D3 ,
It increases calcium absorption from intestine and kidneys too
Vitamin D is also a key factor in mineralization of bone
Melanin opposes UV-B absorption so people with dark complexion needs more time in sun
Deficiency – can cause rickets ,osteomalacia (decreased mineralization of bones),osteoporosis (proportionate loss of both mineral and organic matrix)
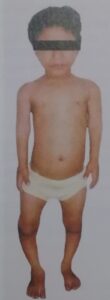
Clinical features may represent as
•Genu valrum
- Genu valgum
*Swelling of wrist
*Delayed closure of anterior fontanelle
*Presence of craniotabes(soft skull bones)
*Delayed dentition
*Harrison’s sulcus (indentation of ribs)
Evaluation for rickets:-
Serum calcium low or normal
Serum phosphate low
Alkaline phosphatase low
Management:-
- Daily requirement- 400 IU
*Treatment of ricket due to malnutrition requires vitamin D in high doses such as 60000 IU of vitamin D daily or on alternate days upto the maximum dose of 600000 IU
VITAMIN E
Vitamin E is naturally occurring membrane antioxidant , it prevents polyunsaturated fatty acids from getting oxidised oxygen free radicals
Hence it’s deficiency and cause , muscle weakness , neuropathy and hemolytic anemia
One of the most common presentations of vitaminE deficiency is hemolytic anemia , in such cases if iron supplement given in excess it can cause exacerbation of haemolysis unless vitamin E is also administers
Being a fat soluble vitamin , children suffering from fat malabsorption are at high risk of its deficiency
High doses of vitamin E can work as antagonist of vitamin K
Management and nutritional requirement:-
Daily need in normal infants is 0.4micrograms/ kg body weight /day
In premature infants 15-20micrograms /day is required
VITAMIN K
Vitamin k is present in two forms in body
Vitamin K1- phylloquinone, present in plants
Vitamin K2- menaquinone, synthesized by intestinal bacteria
Vitamin k is helpful in blood coagulation
The main reason behind vitamin K deficiency in infants is that the vitamin K cannot cross the placenta,and the intestinal flora is not developed much in child ,and it is also less synthesized in breast milk
Vitamin K deficiency can occur in patients in oral antibiotics (which cause elimination of gut flora)
Deficiency symptoms:-
Haemorrhagic diseases such as
-Ecchymosis in 1st week life
– GIT bleeding
-nasal bleeding
-umbilical stump bleeding
Diagnostic points:-
PT (prothrombin time)and PTT (partial thromboplastin time) are increased with normal platelet
Management:-
Administration of prophylactic vitamin K is recommended at birth to all normal and healthy newborns at a dose of 0.5-1mg I.M
To prevent hemorrhagic diseases
Contributor- Medico Shashank Gupta




