MEANING
Clavicle is a Latin word. It means KEY. It looks like f in Italic. It is also known as COLLAR BONE.
TYPE
It is placed horizontally. It is the only long bone.
LOCATION
It is present between the junction of neck and thorax. Its anterior aspect lies between the posterior triangle of neck and pectoral region.
PALPATION
It is a subcutaneous bone and can be felt easily in living.
CONNECTIONS
- SCAPULA
- HUMERUS
- SKULL
- STERNUM
- 1ST RIB
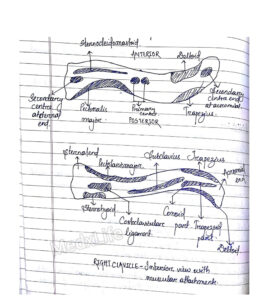
This clavicle forms articulations with medial end which articulates with sternum to form sternoclavicular joint and 1st rib to form costoclavicular ligament. It also forms articulations with lateral end which articulates with acromion process to form acromioclavicular joint.
FUNCTIONS
It helps in transmitting the weight of upper limb to the axial skeleton.
It helps in forming the boundaries for the cervicoaxillary canal.
It protects the neurovascular bundle. It traverses the canal from the neck to the upper limb.
PRESENTING PARTS
It has shafts in its 2 ends. One is medial end which is the expanded end and other is the lateral end which is the flat end.
SHAFT
It is curved. It is in the shape of letter S towards the convexity forward {medial two thirds} and concavity forward {lateral one third}.
MEDIAL TWO THIRD
4 SURFACES
ANTERIOR
POSTERIOR
SUPERIOR
INFERIOR
Middle one third of inferior surface has longitudinal groove known as Sub clavian groove. Inferior surface near the sternal end has a rough oval area i.e., attachment of ligament called Costoclavicular ligament.
LATERAL ONE THIRD
UPPER SURFACE- SUPERIOR
LOWER SURFACE- INFERIOR
Presents – identifiable ANTERIOR & POSTERIOR BORDERS
ANTERIOR BORDER – DELTOID TUBERCLE
POSTERIOR BORDER – CONOID TUBERCLE
ROUGH RIDGE – TRAPEZOID RIDGE OR LINE
It has attachments to conoid and trapezoid parts called coraclavicular ligaments which is a strong structure and can suspend weights of upper limb from the clavicle.
ENDS
ACROMIAL END [LATERAL]
STERNAL END [MEDIAL]
ACROMIAL END [LATERAL]
It is a flat end.
It presents a smooth articular facet.
It articulates the acromion process to form acromioclavicular joint.
Coracoid process of scapula forms the coraclavicular ligament.
MEDIAL END [STERNAL]
Quadrilateral like structure.
Articulates with the manubrium of sternum attached with 1st rib by costoclavicular joint.
It also takes part in sternoclavicular joint.
Palpable landmark
There is a space between the sternal ends i.e. right clavicle and left clavicle called suprasternal notch or space of burns
DETERMINATION OF SIDE OF THE BONES
ACROMIAL END – flat facing laterally
STERNAL END – quadrilateral facing medially
MEDIAL 2/3RD OF THE SHAFT – convexity forward
MEDIAL 1/3RD OF THE SHAFT – concavity forward
INFERIOR SURFACE – longitudinal subclavian groove in middle
CLINICAL APPLICATION
FEATURES OF CLAVICLE
Common bone to be fractured
In 85 % of case, the fracture occurs between the junction of medial two thirds and lateral one third which is the weakest point.
CLEIDOCRANIAL DYSOSTOSIS
Developmental disorder
Affects the membranous bones like skull, clavicle, teeth
Condition – clavicle is absent or defective
GREENSTICK FEATURES OF CLAVICLE
Fracture of a tender or a fracture of young bone, soft and pliable like a green stick.
Initially bends then breaks
In this case the clavicle is slender and thin
It completes the ossification in 20-25 years of fracture which is incomplete.
It resembles the bent branch of a tender plant hence known as green stick and when get fractured gets disconnected and merely hangs.
Contributor- Medico Abinash Jena




