DEFINITION: – Carbohydrates are defined as the polyhydroxyaldehydes / ketones / compounds which produce them on hydrolysis.
CLASSIFICATION OF CARBOHYDRATES:-
The other name of carbohydrates is saccharides. These saccharides are majorly classified into 3 types.These are as follows :-
MONOSACCHARIDES
OLIGOSACCHARIDES
POLYSACCHARIDES
MONOSACCHARIDES:-
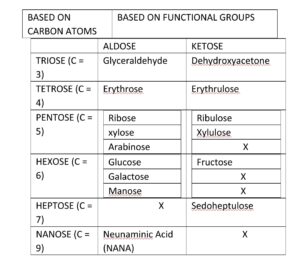
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates. The general formula for these types of carbohydrates is Cn(H2O)n. it cannot be hydrolyzed further. On the basis of no. of carbon atoms present and the functional group present, these monosaccharides are classified.
OLIGOSACCHARIDES:-
Oligosaccharides are the carbohydrate which produces 2 to 10 monosaccharide units on hydrolysis. This contains multiple sugar units i.e., SIALIC ACID and NANOSE. It is present in the glycoproteins such as the immunoglobulin and the blood group substances. It is also present in the glycolipid that is gangliolipids. On the basis of no. of monosaccharides unit present in them these oligosaccharides have 2 subclasses. These are DISACCHARIDES and TRISACCHARIDES.
DISACCHARIDES:-
Disaccharides are the carbohydrates made up of 2 monosaccharides unit. These disaccharides can be reducing or non-reducing.
REDUCING UNITS:-
Reducing units are the units in which only one of the two functional groups are involved and they help in the glycosidic bond formation.
The examples of reducing disaccharides are as follows:-
Maltose – Glucose α 1-4 glucose
Isomaltose – Glucose α 1-6 glucose
Lactose [milk sugar] – Galactose β 1-4 glucose
Lactulose [oxidative laxative] – Galactose β 1-6 fructose
NON REDUCING UNITS:-
Non reducing units are the units in which both the functional groups are involved and they help in the glycosidic bond formation.
The examples of non-reducing disaccharides are as follows:-
Sucrose [cane sugar] – Glucose α 1 – β 2 fructose
Trehalose [ssugar of insect haemolymph , yeast and fungi] – Glucose α 1 – α 1 glucose
TRISACCHARIDES:-
Trisaccharides are the carbohydrates which are made up of 3 monosaccharides unit.
Examples of trisaccharides are as follows – Maltotriose – α – 1 – 4 glucose , glucose , glucose
POLYSACCHARIDES:-
These are the carbohydrates in which more than 10 monosaccharides unit are present. These polysaccharides are divided into 2 types. These are Homopolysaccharides and heteropolysaccharides.
HOMOPOLYSACCHARIDES :-
Homopolysaccharide units are the polysaccharides which are having only identical monosaccharide units.
Examples of homopolysaccharides are as follows
STARCH
GLYCOGEN
DEXTRON
DEXTRIN
CELLULOSE
INULIN
CHITIN
HETEROPOLYSACCHARIDES :- Heteropolysaccharides are the polysaccharides which are having different types of monosaccharides unit.
Examples of heteropolysaccharides are as follows :-
Hyaluronic acid
chondroitin sulphate
heparan sulphate
heparin
dermatan sulphate
keratan sulphate
Contributor- Medico Abinash Jena