DEFINITION OF AGNIKARMA–
त्वऽ.मांससिरास्नायुसंध्यस्थिस्थितेऽत्युग्ररुजि
वायौ ।
Thermal Cautery should be done in presence of very severe pain in the skin, muscles, veins, ligaments, joints
and bones caused by vata (aggravation).
(SUSHRUTA SAMHITA – SUTRASTHANA –
CHAPTER 12, VERSE 10)
• The AGNIKARMA means the application of AGNI(heat).
- Agnikarma involves a procedure whereby heat is transferred to the body using the metal road or needles in an aseptic manner.
- The Agnikarma (Thermal Cautery) has been described in the Ayurvedic literature of Sushrut Samhita, which is written by the legendary Vadic Indian Surgeon Sushruta, often referred to as the father of modern surgery, where he has described Agnikarma’s effect on disorder ofAsthi(bone), Sandhi (joint), and Snayu (ligament/tendon).

PHYSIOLOGY OF PAIN IN AYURVEDA–
• Pain is an uncomfortable feelings that tells you something may be wrong. It can be steady, throbbing, stabbing, aching, pinching or described in many other way. Sometimes, its just a nuisance, like a mild headache.
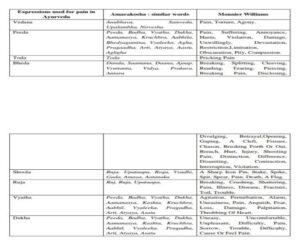
• In Ayurveda, pain is denoted as PEEDA, VEDANA, RUJA, SHOOLA, RUK, TODA,
BHEDA, VYATHA,ETC. As defined in coming
table: TABLE
WHERE THE PAIN RESIDES?
• CHARAKA says VEDANA are prescribed in MANA(mind) and DEHA(body) involving
INDRIYA (sensory organs).
• They are not perceived in KESHA(scalp hair), LOMA(body hair), NAKHAAGRA(tip of nails),
ANNA MALA(feces), ANNA DRAVA(urine) (CH SH 1/136)
• So for the perception of pain, the role of INDRIYA along with MIND is very important.
HOW THE PAIN IS PERCIEVED?
• The function of the pain sensory system is to protect the body and maintain homeostasis. It does this by detecting,
localizing, and identifying potential or actual tissue-damaging processes. Each spinal nerve conducts impulses
from a specific area of the skin called “a dermatome” and the somatosensory cortex is “mapped” to correspond to
areas of the body so that the source of Pain can be interpreted in the brain.
• During the process of sensing the pain, primary afferent nociceptors have two tasks. The first is to transduce a
damaging or potentially damaging stimulus, whether mechanical, thermal, or chemical, into the code used by the
nervous system, electrical potentials.
• The second task of the primary afferents is to transmit that information into the central nervous system for
processing. (Bahya tvacha/sparshanendriya to Mana to Buddhi to Atma) It is said that when communicated
through the Karana (tools or instruments), karta i.e. Atma gets the realization of Karma, vedana and budhi (Ch Sh
1/56). Mana (Mind), Buddhi (Intellect), Sense organs (Dnyanendriya) and Functional organs (Karmendriya) are
the tools or Karana. So for the sensation of Vedana, the tools like Mana (Mind), Buddhi (Intellect),
• Sense organs (Dnyanendriya) and Functional organs (Karma Indriya) play a major role. It is said that though
Atma (soul) gets all the knowledge or information and it is vibhu (i.e. spread all over). But still it cannot perceive
the knowledge until the subjects are perceived by their respective sense organs through Mind. For that Mind has
to be in constant touch with the sparshanendriya (skin) (Ch Sh 1/56).
• In Ayurveda sparshanendriya i.e. skin has spread all over the body internally as well as external. Every single cell
and cell organelle has the cover of sparshanendriya. Mind gets attached to every single sense to carry it to Buddhi
for further processing. After receiving this sensory inputs of every stimuli whether it good or bad, buddhi
interprets it and suggest Ahankaara to proceed in the said subject. (Ch Sh 1/ 22, 54, 55) That is why it is said that
vedana are expressed by Sparshanendriya Sparsha and Manasa Sparsha (Ch Sh 1/ 133).
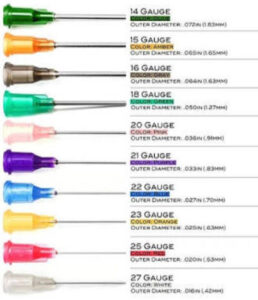
INSTRUMENTS IN AGNIKARMA–
• PANCHLOH SHALAKA

• DISPOSIBLE NEEDLES
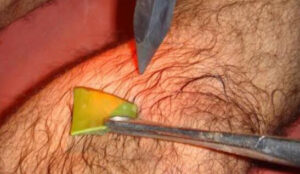
AGNIKARMA PROCEDURE-
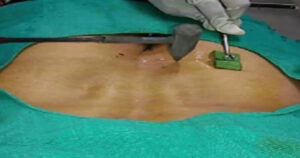
- WITH SHALAKA–
-Pt. should taken up to the opd table or minor ot table for further procedure, with (laghu)-light diet intake.
-After that pt. should be lied in according to the affected part of body.
-Before operating pt should be given a test dose for checking the reactivity of pt. Inj t.t. should be adminstrated to the pt.
-With all strerlized instruments i.e. agnikarma panchloh shalaka , forceps, artery forceps, cotton and swaps.
-Paint the affected area with betadine or jatyadi teilm solution .
-With the rules of agnikarma shapes according to shusruta ,touch the red hot shalaka for a few seconds.
-After that use alovera pulp or antiburn cream on the spot.
-One can proceed the procedure with alternate day according to pt.
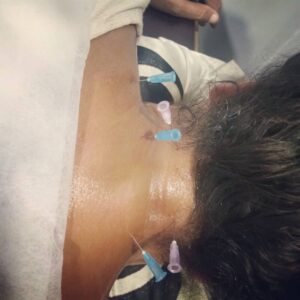
2. WITH NEEDLES (viddh karma)–
-Same pre operative management should be done in case with needles too.
-Choose the needle according the anatomical-marma structure.
-Insert the needle around 1-3 cms of actual marma becauz marma consist of prana(life) so don’t go in marma.
-After that cut the upper part of needle with needle cutter.
-Then give heat to the upper part of needle around to less than 100degrees i.e.
the part of needle become red hot .
-That red hot of upper part of needle covert mechanical energy into metabolic energy and opens the stiffed peshi-muscle and balances the vata doshas that decreases the pain in affected area.
-After 45 minutes of procedure gentally out the needle with the help of artery forceps gentally.
-If blood came out of that point of needling and gradually stops after some times, then it indicates rakmokshanam/bloodletting of diseases blood to.
How to Perform Agnikarma ?
Contributor- Dr. Mohit Sandhu





Very well explained 👏👏
Beautifully described this topic🔥💯Happy to read many more articles like this🙏🏻
😍😍😍🔥🔥🔥
Congratulations dear
Great, loved it sir, Keep growing
Jai Ayurveda
Wow such a wonderful description..